In digital printing, whether it is direct inkjet printing with disperse dyestuff on polyester fabrics, or transfer printing after printing, or inkjet printing on natural fibre fabrics such as cotton, linen, silk and wool, the industry generally adopts single-sided inkjet printing. For reasons of ink, paste or inkjet printing technology, there are three common defects in digital printing products:
- “white out”: for digital inkjet printing products on stretch fabrics such as swimwear, shoe uppers and home textiles, stretching or pressing the fabric in the opposite direction by hand will reveal a white background in the pattern, which seriously affects the quality of the product.
- “Flip”: Due to the poor penetration of conventional inkjet printing inks, the print only penetrates the surface of the fabric, making it difficult to penetrate the interior. This results in white threads showing through the eye of the stitches on garments and scarves sewn with this print. In particular, scarves made from fabrics with high yarn twist and a loose fabric structure such as georgette and double crepe are more likely to show white threads in the pattern during wear.
- “Difference between front and back: conventional single-sided inkjet printing, pattern pulp can not effectively penetrate the reverse side of the fabric, resulting in a large colour difference between the front and back of the pattern of heavy fabrics. Although many manufacturers have introduced penetration ink or penetration inkjet printing process, but also difficult to solve such problems. In addition, inkjet printed fabrics have long had a single presentation, i.e. only one side of the fabric is printed with a pattern and the other side is left blank, which greatly limits the expression of product design intentions and the variety of styles available.
In order to solve the above defects, based on the precise positioning inkjet printing, we have done a lot of experiments, through the development of pre-treatment paste, as well as digital printing and post-printing process technology improvement, summed up the use of digital precision positioning inkjet printing technology, so that the ink can penetrate from the front and back of the fabric to the inside of the fabric at the same time, to achieve both good fineness, but also to solve the problem of fabric lining yarn It also solves the problem of poor colour fastness of double-sided digital printing products and ensures the quality of double-sided digital printing products, thus opening up the expression of the intention of digital printing product design and the diversity of product styles. Due to the large number of process points and auxiliaries involved in double-sided digital printing, this study only introduces the double-sided digital printing process technology in terms of several key process points and process factors affecting product quality, such as printing blank selection, sizing stock, printing control and post-steaming treatment.
Screening of double-sided digital printing blanks
The key technology for double-sided digital printing is the precise positioning of the digital printing. a) Choose a woven fabric with low deformation and good stability, the fabric should not have tight or loose edges, and the locking line should be consistent with the material of the fabric; b) Control the weft slope of the fabric within 2%, too much weft slope will increase the difficulty of accurate positioning and positioning printing, affecting the quality of the double-sided digital printing product; c) The fabric fibre composition is pure cotton or pure silk, because the blended fabric needs a variety of d) The fabric should not be treated with softness or other coating treatments, as softener, coating glue and other materials affect ink penetration and colour uniformity; e) Choose fabrics with the same structure on both sides, such as double-sided satin, twill silk and double crepe, to avoid different colours and shapes of the printed pattern caused by different fabric tissues. The colour homogeneity of the print is affected by the difference in lustre and structure of the fabric on both sides. f) The fabric surface p H value is about 7 and the fabric gross effect reaches 1012 cm in 30 min to ensure the wetting and longitudinal penetration of the printing ink on the fabric.
Double-sided digital printing process
After years of production practice, a practical double-sided digital printing process has been formed to meet the production and quality requirements of double-sided digital printing products. Take cotton woven fabric as an example, the double-sided digital printing process is as follows: after refining the fabric whole weft sizing (a dipping, a rolling, rolling residual rate of 75% 85% or so) drying (1 20 ℃ continuous drying, 4 min) front printing pattern drying (70 ℃, 3 min) mirror production reverse graphics positioning reverse printing pattern drying (70 ℃, 3 min) steaming (102 ℃, 12 min) → washing (cold washing 4 5 ℃ washing 9 ℃ washing) Washing (cold water, 4.5 °C, 9 °C, cold water) → drying (continuous drying at 1.25 °C, 4 min)
Pre-treatment process for positioning digital printing
After years of experience with the properties of pastes used in digital printing and double-sided digital inkjet printing, four pastes were selected and the pastes were prepared according to Table 1. The method: add the appropriate amount of water to the container, dissolve the powder in the water, then add the urea and stir to dissolve. Add the paste and stir until there are no lumpy particles, then add baking soda and stir well. The K/S value of the printed fabric at the maximum absorption wavelength was determined by using a colourimeter from AstraZeneca and the K/S value of the front and back of the printed fabric was tested with a colourimeter under a D6 5 light source and the permeation rate was calculated by the formula: permeation rate/% (K/S value of the back of the printed fabric/K/S value of the front of the printed fabric). The permeation rate of the printed fabric was calculated by using the formula: permeation rate/% (K/S value of printed fabric back/ K/S value of printed fabric front) × 100, and the results are shown in Figures 1 and 2.
Table 1 Sizing sizing formulations for cotton fabrics
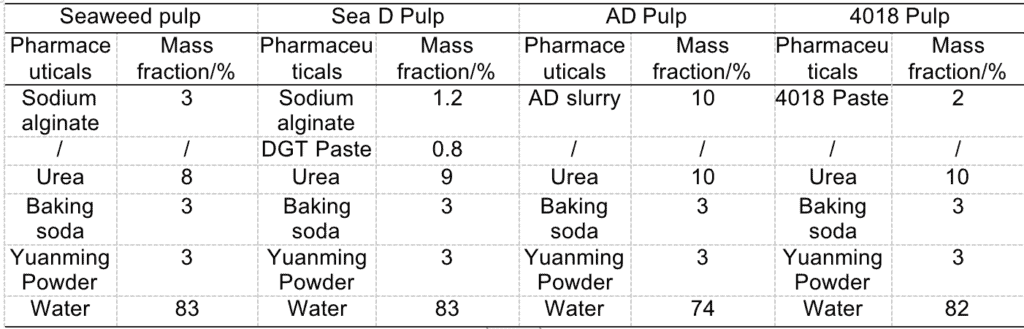
Note: DGT paste is modified starch paste (Shandong Mingyue Chemical Co., Ltd.); AD paste is a mixture of polyacrylate and modified polysaccharide paste (Hangzhou Honghua Digital Technology Co., Ltd.); 4018 paste is a polyacrylate paste (Hangzhou Anuo Chemical Co., Ltd.).
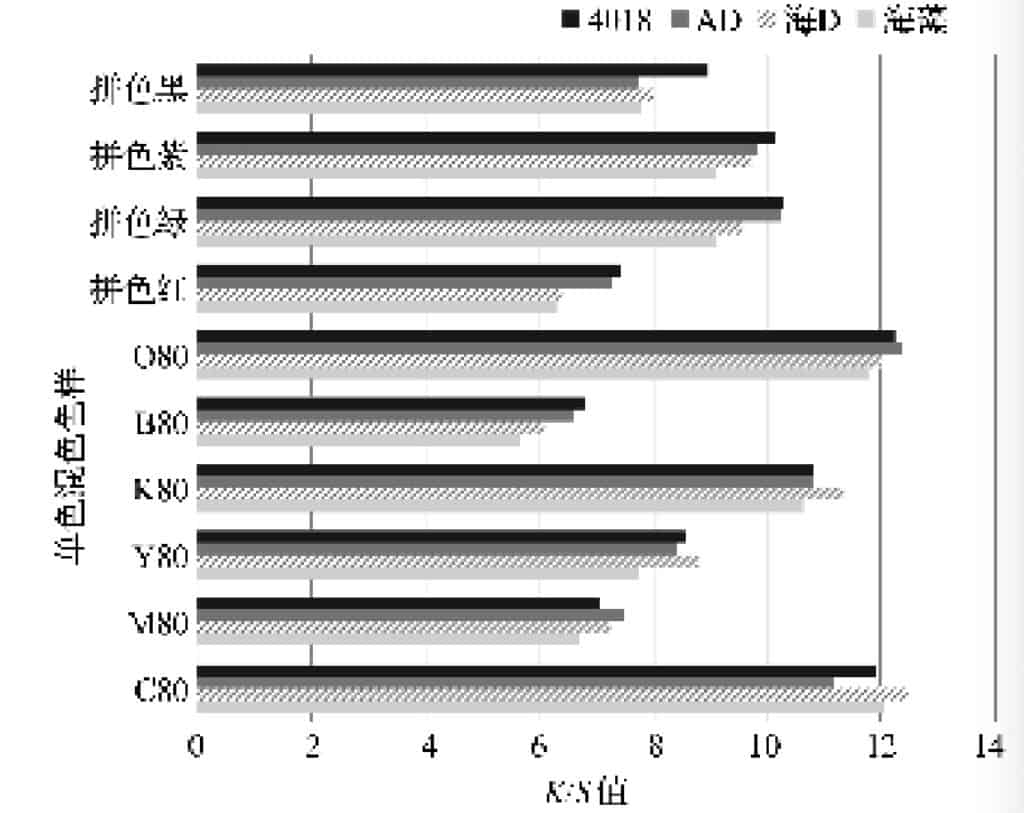
Fig. 1 Effect of four pastes on the K/S value of the printed colour block
Figure 1 shows the K/S values of the colour blocks of the fabric on the four selected pastes for the 10 commonly used monochrome and colour blocking dyes. The horizontal coordinates in Figure 1 are the K/S values of the blocks printed on the medium and dark colours of the commonly used monochrome inks for digital printing as well as the blocks printed with the selected pastes, namely Seaweed Paste, Sea D Paste, AD Paste and 4018 Paste.
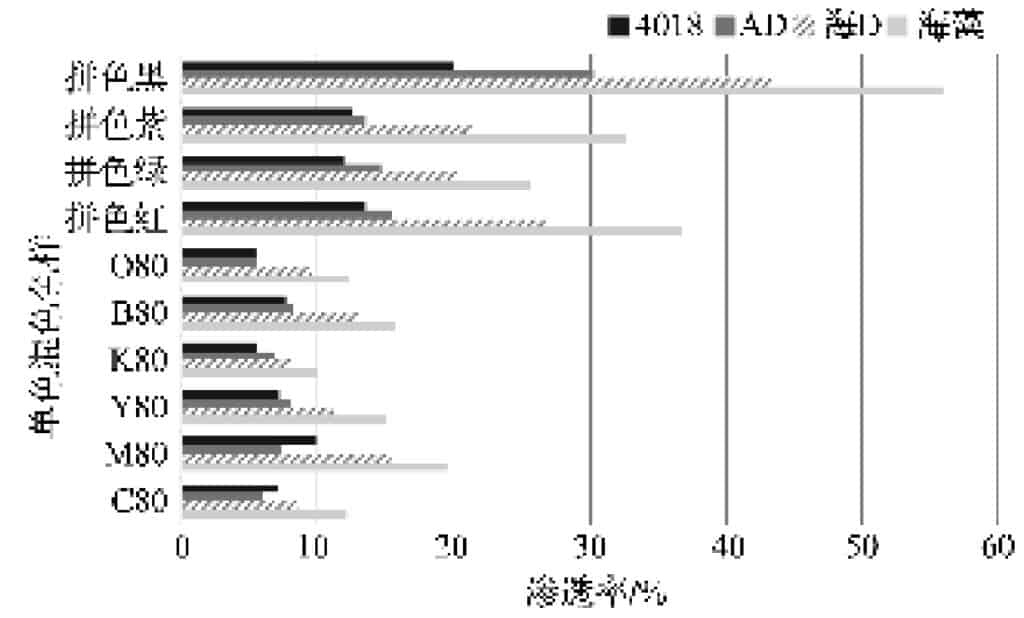
Fig. 2 Permeability of the pattern of the product printed with the four pastes
Figure 2 shows the permeation rates of the four pastes selected above for the 10 commonly used monochrome dyestuffs and colour blocking dyestuffs. Cross-seat
The marker is the commonly used digital printing of monochrome inks for medium and dark colours as well as the colour blocks printed by the colour mixing dyes, the paste is seaweed pulp, sea D pulp, AD pulp, 4018 pulp, and the vertical coordinate is the penetration rate of the corresponding paste colour blocks.
Figure 1 shows that the order of K/S values for print depth is: 4018 paste > AD paste > Sea D paste > Seaweed paste.
Figure 2 shows the order of permeability of the pastes: seaweed pulp > sea D pulp > AD pulp > 4018 pulp.
Compared to single-sided printing, double-sided printing with the same colour has special requirements in terms of paste selection, such as the need for good water-holding properties, especially for thin fabrics, which require higher water-holding properties. The choice of AD and 4018 was based on a combination of permeability, K/S values and experience with the water-holding properties of pastes for double-sided printing.
Printing process for double-sided digital printing
The most critical and difficult aspect of digital printing is the precise positioning of the print on the reverse side. Due to the soft nature of the fabric, the pattern will be distorted when the front is printed and then turned over to print the reverse side.
In this study, Atcamera software was used for precise positioning and pattern conversion, and the printing was carried out on a Honghua DBP-3020 machine with a print accuracy of 600 x 600dpi-2pass or 600 x 600dpi-3pass. There are three aspects of the printing process that require special attention.
a) Create and select a density curve and colour conversion curve to match the double-sided printed fabric. The density curve is a curve that establishes the correspondence between the actual ink volume and the visual effect in order to control the dot gain phenomenon and bleeding of the ink droplets onto the fabric, resulting in an even gradation of the individual inks and a rich layering of the ink to obtain the desired output. The RIP program converts the image RGB colour data into the printer’s C, M, Y, K, B, O and other ink channel data according to the printer’s ICC device colour profile curve. For double-sided printing, both sides have to be inked, so the density curve and colour conversion curve have to be adapted to the control procedure.
b) After setting the positioning point to carry out back side printing need to strengthen the inspection and correction of deflection. This is the focus and difficulty of double-sided inkjet printing, that is, to control the printing process of the overall correction of the pattern and local displacement, requiring continuous inspection and monitoring, the software can not be automatically corrected manually corrected. c) After the print is completed, it should be sealed and stored at room temperature, with a relative humidity of less than 30% for no more than 24 hours, to be steam cleaned.
Illustrations of double-sided digital inkjet printing
Only with a correct understanding of the principles of double-sided printing, a good grasp of the printing machine and software, and enhanced supervision during the production process, can double-sided printed fabrics be printed with complete and accurate positioning on both sides. Through extensive testing of the Smart Positioning System, the positioning error of the front and back side can be controlled to within 0.3 mm and the colour difference between the front and back side can be controlled to more than 4 levels to achieve the double-sided printing objective. Figures 3 – 6 show examples of traditional single-sided and double-sided printing on both sides.
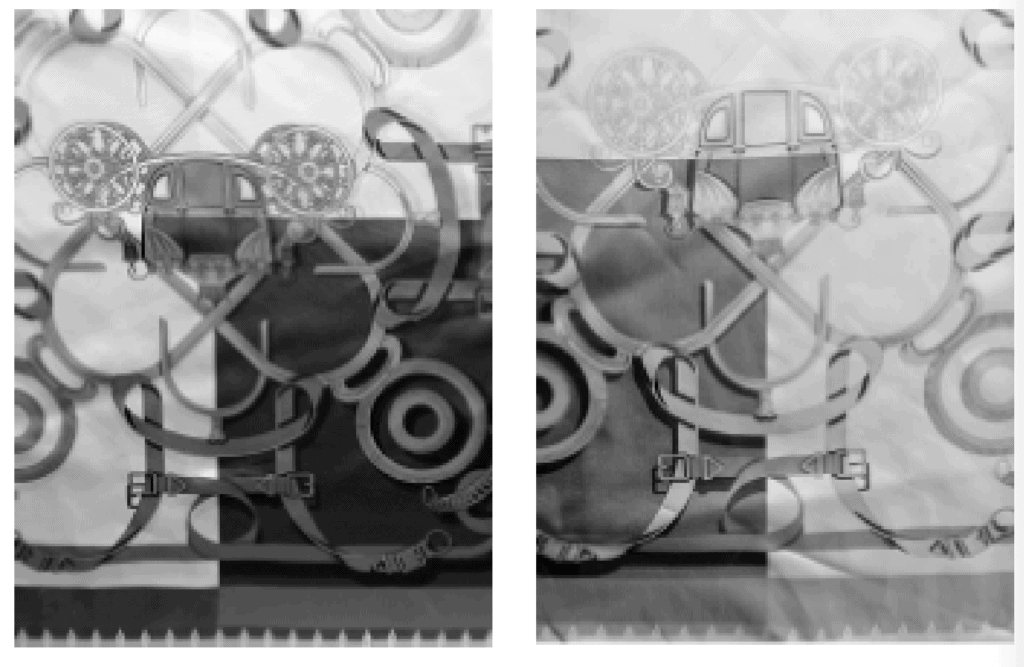
Fig. 3 Single-sided printed front Fig. 4 Reverse side of single sided print
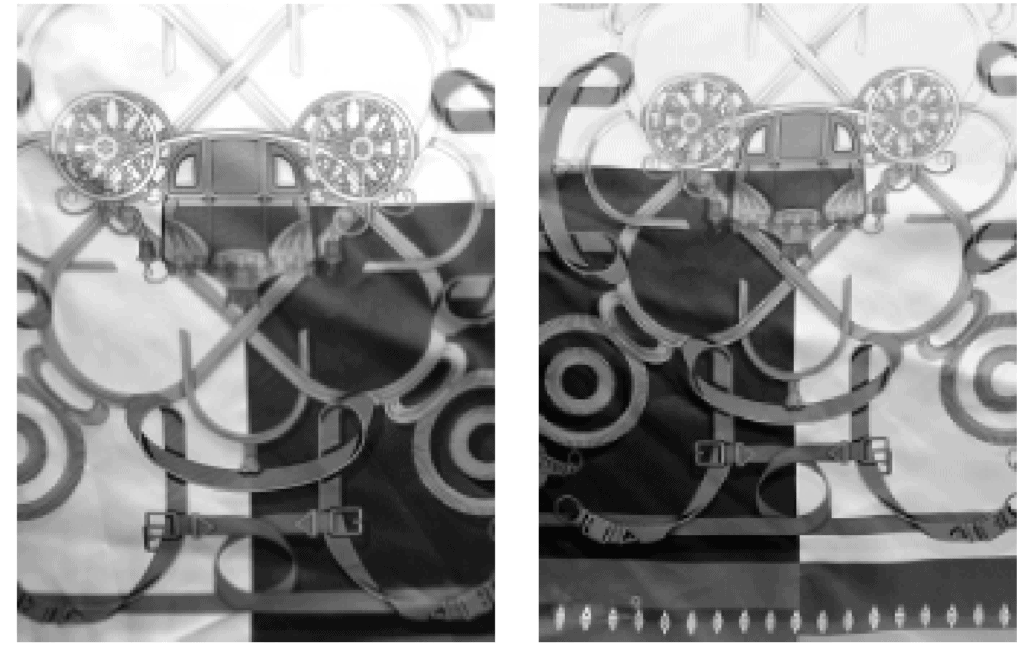
Fig. 5 Double-sided printed front Fig. 6 Reverse of double-sided print
Post-treatment process parameters and analysis
The post-treatment process of double-sided digital printing is similar to that of single-sided digital printing, mainly through the processes of steaming, washing, shaping and winding. The process parameters are as follows:
a) Steaming process for reactive dyestuffs: steaming temperature 1 0 0 1 0 2 °C; steaming relative humidity 80%; steaming time 8 15 min (cotton or silk fabrics).
The key difference between single-sided digital printing and double-sided digital printing is that both sides of the fabric have colour and pattern, so in order to ensure uniformity of colour on both sides, the humidity of the steamer should be kept at 80% relative humidity (plus or minus 5% is optimal).
b) Washing process for reactive dye printing :
Cold water washing, counter-current washing for 1 5 min → warm water washing at 4 0 5 0 °C → soaping in warm water at 4 0 5 0 °C → cold water washing → stentering and shaping.
Soaping process: non-foaming soaping agent 4 g/L.
Soaping time: 5-8 min (soaping time can be increased or decreased depending on the thickness of the fabric).
Soaping temperature: cotton fabrics generally 8595 °C, silk fabrics generally 80 -90 °C.
Due to the large amount of paste and ink attached to the double-sided print, it is necessary to extend the washing time and increase the soaping temperature of each wash, so that the paste and floating colours can be washed out thoroughly and the quality of the product can be improved.
c) Stretching and shaping
Drying process after dipping and rolling. The amount of colour fixing agent CEO is controlled at 0.3% to 0.5% depending on the colour shade, and the amount of softener PPF is controlled at 0.2% to 0.5% depending on the fabric thickness and handfeel requirements. The shrinkage rate is controlled within 3%.
Conclusion
Double-sided precision positioning digital printing is a brand new process, through the selection of suitable fabrics for digital printing, pre-treatment, front digital printing, reverse precision positioning digital printing and post-treatment processes when one end is stretched and one end is slackened to produce a bend in the rope.
a) Due to the speed limitation of the motor, the range of adjustment is not sufficient to achieve the anti-overlap function at high winding speeds (over 1,000 m/min) by means of transverse speed regulation, which tends to form hard edges . This can be improved by cross-varying the speed between the two reversing positions.
b) The distance between the yarn-guiding hook and the winding surface should be reduced as much as possible. In practice, when the distance between the yarn-guiding hook and the winding surface is 20 mm, the yarn is well formed.
c) The transverse dimensional stability of the cylinder yarn is also related to the winding speed, which is large and slightly longer in size, and should be taken into account when adjusting the process.
























